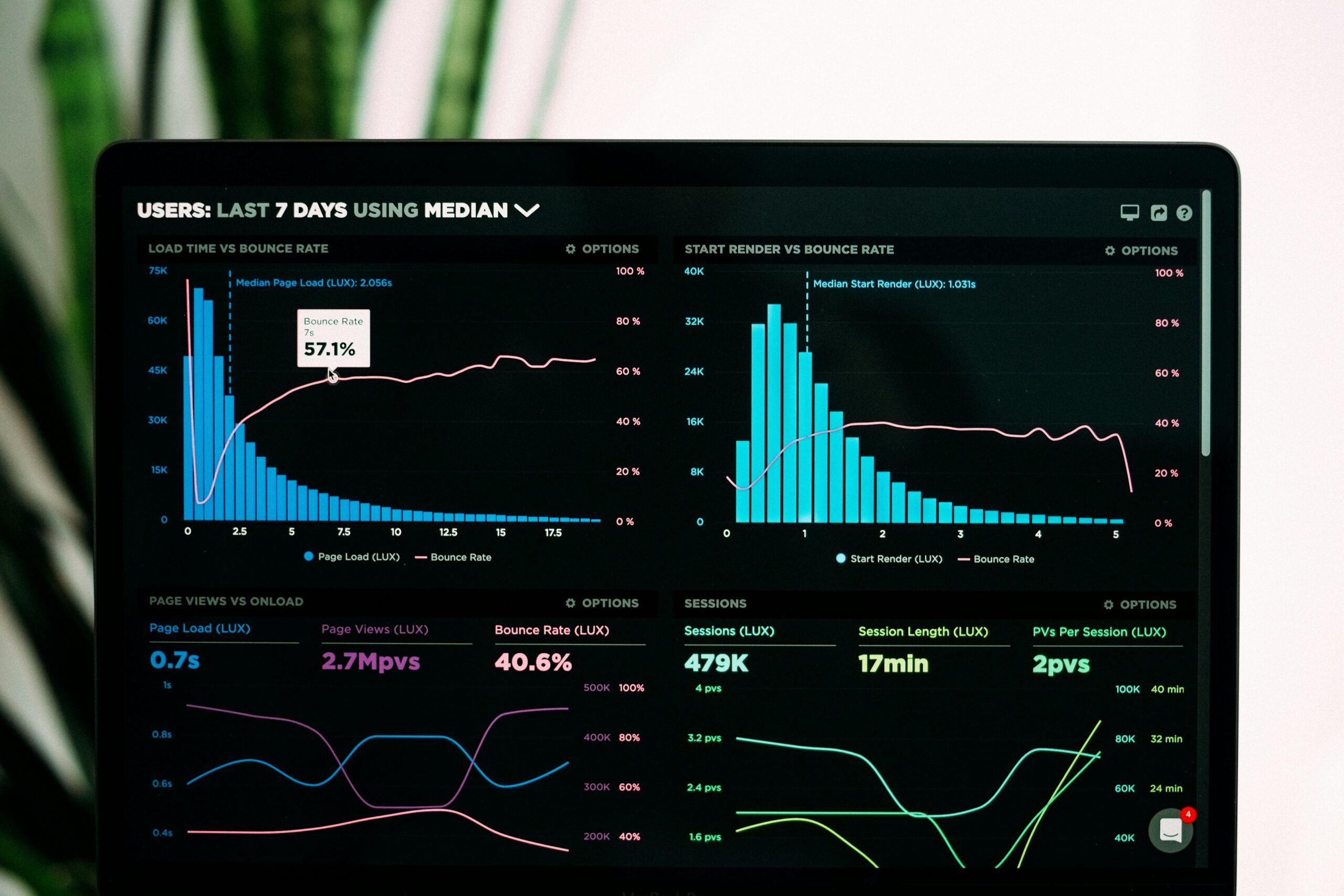
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
- Overview
- Production Information
- Getting Started
Guided Assembly
Guided assembly integrates digital tools and technologies into the assembly process to provide
step-by-step instructions, visual aids, and interactive assistance to human operators.
step-by-step instructions, visual aids, and interactive assistance to human operators.
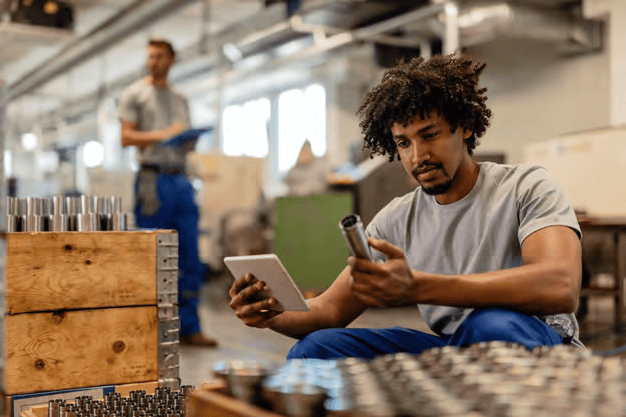

Digital Work Instructions
Instead of relying solely on paper-based or static instructions,
operators receive digital instructions on screens, tablets, or wearable
devices. These Instructions can include text, images, videos, and
animations that guide operators through each assembly step.

Augmented Reality (AR)
AR technology overlays digital information, such as arrows, labels, and visual cues, onto the physical workspace. This helps operators understand where components should be placed, how they should be oriented, and how they fit together.
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR technology overlays digital information, such as arrows, labels, and visual cues, onto the physical workspace. This helps operators understand where components should be placed, how they should be oriented, and how they fit together.


Sensors and Feedback
Sensors can provide real-time feedback on various assembly
parameters, such as torque applied, alignment accuracy, and component presence. This ensures that each step is performed correctly, and any deviations are immediately detected.

Benefits of Guided Assembly
Reduced errors, faster training, increased efficiency, flexibility and
adaptability, data collection and analysis, consistency, real-time information, and adaptive manufacturing.
Benefits of Guided Assembly
Reduced errors, faster training, increased efficiency, flexibility and
adaptability, data collection and analysis, consistency, real-time information, and adaptive manufacturing.

Experience a Live Demo
See how you can make your manufacturing smarter